
|
|
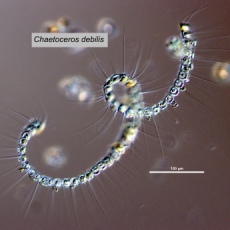
| C. convolutus | C. debilis |
|

|
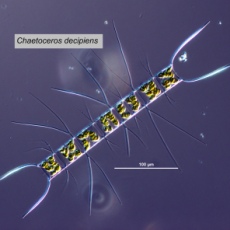
| C. decipiens | C. didymus |

|

|
| C. radicans | C. similis |

|
|
| C. socialis |
Classification
(Guiry and Guiry 2012)
Lifestyle
Description
Girdle
In diatoms, the portion of the cell wall between the two valves of a cell; made up of intercalary bands (bands closest to the valves) and connecting bands (bands in the middle of the girdle). In dinoflagellates, the equivalent of a cingulum or transverse furrow (Horner 2002).
girdle view and elliptical in CloseValve
In diatoms, the structurally distinct halves of the cell wall (Becker 1996).
valve view (elliptic cylinder), with two spines arising from each valve. Adjacent cells are linked by the crossing or touching of the spines near the base (Cupp 1943). Cells are yellow-brown in colour (Guiry 2012).Measurements
Apical
(axis, spine) The region of the apex or point. Refers to the most anterior point or region of the cell (HPP 2003).
(apical axis): 2 - 85 μmLength Close
Pervalvar axis
The axis through the centre point of the two valves of a frustule. This axis is perpendicular to the valve face.
(pervalvar axis): 2 - 45 μm(Hasle and Syvertsen 1997, Kraberg et al. 2010)
Key to local species
Aperture
"In some diatoms, the space between the valves of adjacent cells in chains" (Horner 2002).
aperture; spines very straight and extend out diagonally. C. similisHarmful effects
Habitat
Distribution
Environmental Ranges
Temperature range (°C): -1.952 - 29.468
Nitrate (μmol L-1): 0.053 - 34.037
Salinity: 18.564 - 37.775
Oxygen (mL L-1): 4.139 - 9.192
Phosphate (μmol L-1): 0.046 - 2.358
Close
Silicic acid
A general term to describe chemical compounds containing silicon, oxygen and hydrogen with a general formula of [SiOx(OH)4-2x]n. Diatoms polymerize silicic acid into biogenic silica to form their frustules (Azam and Chisholm 1976).
Silicate (μmol L-1): 0.648 - 92.735(OBIS 2012, cited in EOL 2012)
References
Cupp, E. E. 1943. Marine Plankton Diatoms of the West Coast of North America. University of California Press. Berkeley, California. 238.
Encyclopedia of Life (EOL). 2012. Chaetoceros. http://eol.org/pages/12010/overview. Accessed 18 Mar 2012.
Guiry, M. D. 2012. Chaetoceros Ehrenberg, 1844. http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=148985. Accessed 18 Mar 2012.
Guiry, M. D. and Guiry, G. M. 2012. Chaetoceros Ehrenberg, 1844: 198. http://www.algaebase.org/search/genus/detail/?genus_id=43689. Accessed 18 Mar 2012.
Hasle, G. R. and Syvertsen, E. E. 1997. Marine diatoms. In: Tomas, C. R. (ed.) Identifying Marine Phytoplankton. Academic Press, Inc., San Diego. 5-385.
Kraberg, A., Baumann, M. and Durselen, C. D. 2010. Coastal Phytoplankton: Photo Guide for Northern European Seas. Verlag Dr. Friedrich Pfeil, Munchen, Germany. 204.
Ocean Biogeographic Information System (OBIS). 2012. Chaetoceros. http://www.iobis.org/mapper/?taxon_id=611649. Accessed 18 Mar 2012.
