




|
Synonym(s)
Classification
(Guiry and Guiry 2012)
Lifestyle
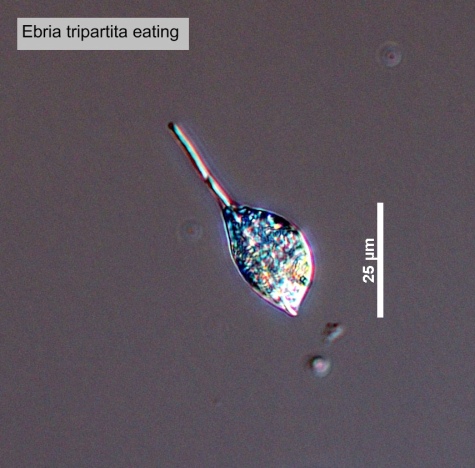
Description
Measurements
Similar species
Harmful effects
Habitat
Estuary
The area where a river meets the ocean. Often characterized by high sediments, high nutrient levels, salinity fluctuations and tidal mixing.
estuaries and inland saline lakes (Ernisse and McCartney 1993, cited in Westman 2000).Distribution
Cold to temperate regions (Horner 2002).
Information not available.
Information not available.
Growth conditions
Environmental Ranges
Temperature range (°C): -1.859 - 23.653
Nitrate (μmol L-1): 0.349 - 9.600
Salinity: 17.940 - 37.775
Oxygen (mL L-1): 4.947 - 8.948
Phosphate (μmol L-1): 0.051 - 1.164
Close
Silicic acid
A general term to describe chemical compounds containing silicon, oxygen and hydrogen with a general formula of [SiOx(OH)4-2x]n. Diatoms polymerize silicic acid into biogenic silica to form their frustules (Azam and Chisholm 1976).
Silicate (μmol L-1): 1.595 - 29.876(OBIS 2012, cited in EOL 2012)
Bloom characteristics
References
Encyclopedia of Life (EOL). 2012. Ebria tripartita. http://eol.org/pages/898673/overview. Accessed 21 Jan 2012.
Ernisse, J. and McCartney, K. 1993. Ebridians. In: Lipps, J. H. (ed.) Fossil prokaryotes and protists. Blackwell, Cambridge, MA, USA. 131-140.
Guiry, M. D. and Guiry, G. M. 2012. Ebria tripartita (Schumann) Lemmermann. http://www.algaebase.org/search/species/detail/?species_id=56482. Accessed 21 Jan 2012.
Hargraves, P. E. 2002. The ebridian flagellates Ebria and Hermesinum. Plankton Biology and Ecology. 49(1): 9-16.
Horner, R. A. 2002. A Taxonomic Guide To Some Common Phytoplankton. Biopress Limited, Dorset Press, Dorchester, UK. 200.
Ocean Biogeographic Information System (OBIS). 2012. Ebria tripartita. http://www.iobis.org/mapper/?taxon_id=436987. Accessed 21 Jan 2012.
Rhodes, R. G. and Gibson, V. R. 1981. An annual survey of Hermesinum adriaticum and Ebria tripartita, two Ebridian algae in the lower Chesapeake Bay. Estuaries. 4(2): 150-152.
Westman, P. 2000. The siliceous microalgae Dictyocha speculum and Ebria tripartita as biomarkers and palaeoecological indicators in Holocene Baltic Sea sediments. Geological Society in Stockholm (GFF). 122(3): 287-292.
