

|
Synonym(s)
Classification
(Guiry and Guiry 2011)
Lifestyle
Protist
A diverse group of eukaryotic microorganisms which range from "animal-like" protozoa to "plant-like" algae. This is an older, informal term referring to many simple organisms that do not fit well into the kingdoms of plants, animals or fungi. This means that diatoms, dinoflagellates, amoebae, ciliates, slime moulds, and many other groups of organisms can be called protists.
protists using feeding tube (EOL 2011). It reproduces asexually by binary fission (EOL 2011).Description
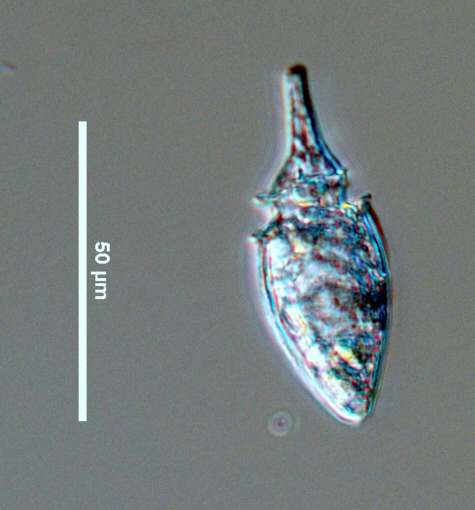
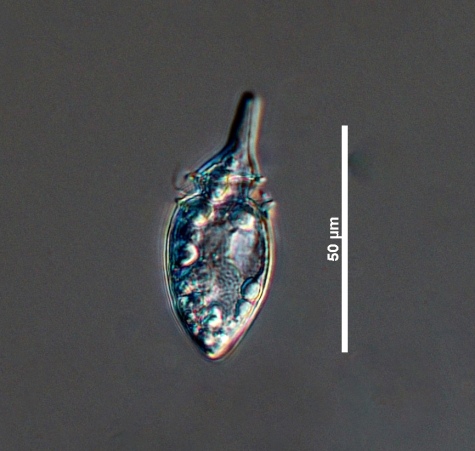
Subfusiform
Describes a tube shape that widens at both ends and tapers in the middle.
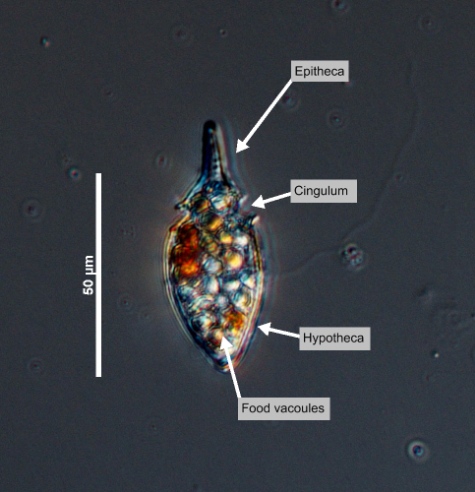
subfusiform and laterally compressed. Cells are always longer than they are wide: they are 60 - 68 μm long and 16 - 24 μm wide. The cell's CloseCingulum
(dinoflagellates) "In dinokont dinoflagellates, a furrow encircling the cell one or many times" (Horner 2002). It is also known as the girdle or transverse groove and may be located at, above, or below the midpoint of the cell with the left and right ends meeting or displaced form one another (Horner 2002). In diatoms, this term describes the collective elements of a diatom girdle: "The cingulum is made up of delicate silica bands that join the two valves of a frustule. Most diatoms possess a cingulum, although some may not" (Spaulding et al. 2010).
cingulum is about ⅓ cell length from the apex. The CloseEpitheca
In thecate dinoflagellates, the anterior part of a dinokont cell above the cingulum. The equivalent of epicone for naked dinoflagellates.
epitheca is narrower than the CloseHypotheca
In thecate dinoflagellates, the posterior part of a dinokont cell above the cingulum. The equivalent of a hypocone for naked dinoflagellates.
hypotheca (Smithsonian 2011) being slightly asymmetrical, ending in a straight CloseHorns
The apical or antapical extensions found in some armoured dinoflagellates; they contain cytoplasm, are covered in thecal plates and can be hollow or partially solid (Horner 2002).
horn (Horner, 2002). The hypotheca has CloseLateral
Relating to a side-to-side direction.
laterally compressed sides with a blunt point at the tip. The cell has a very short CloseSulcus
"In dinokont dinoflagellates, the longitudinal area on the ventral surface that forms a furrow or depression and houses the longitudinal (trailing) flagellum" (Horner 2002).
sulcus with narrow CloseSulcal list
(left and right) In dinokont dinoflagellates, a well-defined groove on the ventral surface that is supported by ribs.
sulcal lists. O. oxytoxoides is heterotrophic and hence does not have any chloroplasts, so its colour depends on the colour of its food (Horner 2002). It looks like a spindle or an elongated spinning top.Measurements
Width: 16 - 24 μm
(Smithsonian 2011)
Similar species
Harmful effects
Habitat
Distribution
Environmental Ranges
Temperature range (°C): 19.811 - 23.653
Nitrate (μmol L-1): 0.349 - 8.097
Salinity: 34.513 - 35.114
Oxygen (mL L-1): 4.863 - 5.068
Phosphate (μmol L-1): 0.077 - 1.151
Close
Silicic acid
A general term to describe chemical compounds containing silicon, oxygen and hydrogen with a general formula of [SiOx(OH)4-2x]n. Diatoms polymerize silicic acid into biogenic silica to form their frustules (Azam and Chisholm 1976).
Silicate (μmol L-1): 2.873 - 6.865Bloom characteristics
References
Encyclopedia of Life (EOL). Oxyphysis oxytoxoides Kofoid 1926. http://www.eol.org. Accessed 18 Sept 2011.
Guiry, M. D. and Guiry, G. M. 2011 Oxyphysis oxytoxoides Kofoid 1926. http://www.algaebase.org/search/species/detail/?species_id=45678. Accessed 24 Sept 2011.
Horner, R. A. 2002. A Taxonomic Guide To Some Common Phytoplankton. Biopress Limited, Dorset Press, Dorchester, UK. 200.
Smithsonian Institution. 2011. Oxyphysis oxytoxoides Kafoid 1926. http://www.sms.si.edu/irlspec/Oxyphy_oxytox.htm. Accessed 16 Oct 2011.
